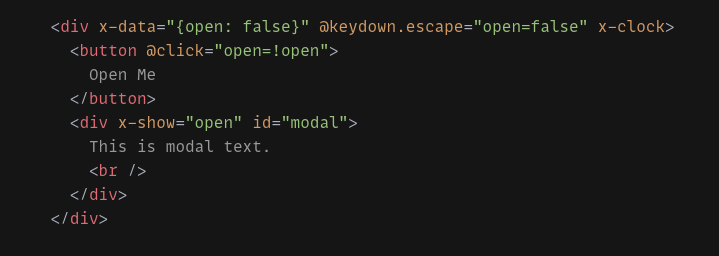
Access AlpineJS x-data variable outside scope
I was big fan of jQuery before I started using AlpineJS!. Alpine is so easy and seamless that I fell in love with it instantly. One more thing that you might want to consider is its size. Alpine is very small in comparison of jQuery, Vue, Angular etc. Alpine was previously called Tailwind of JavaScript. If you don’t know about Tailwind, Man you should read it. If you wanted to learn about AlpineJS basics and other concepts click here....